Robotic Process Automation, commonly known as RPA, is transforming the way organizations work. From ai in itsm - IA en ITSM to optimizing business workflows, RPA hands repetitive computer tasks over to software robots, allowing businesses to move faster, cut costs, and free people to focus on higher-value, creative, and strategic work. It also plays a crucial role in modern AI customer engagement strategies, helping companies deliver faster, more personalized experiences.
Beyond streamlining repetitive tasks, RPA connects seamlessly with cloud computing with AI, enabling businesses to process large volumes of data securely and efficiently without the need for heavy on-site infrastructure. When combined with advanced computer technology, organizations can automate complex processes across multiple systems, improving accuracy and productivity.
In the realm of marketing, RPA enhances marketing with AI and digital marketing using AI by automating customer segmentation, campaign reporting, and personalized outreach. This allows marketing teams to focus on creativity and strategy while automation handles the repetitive, time-consuming tasks. Similarly, in finance, financial AI powered by RPA can manage transaction monitoring, reporting, and compliance checks, reducing errors and enabling faster decision-making.
If you have ever copied data from one system into another, clicked through the same screens dozens of times a day, or generated the same report every week, you have already met the kind of work RPA was born to handle. This guide explains what is rpa, how it works, where it shines, and how you can start using it in your own organization.
Top 10 AI Contact Center Solutions for Businesses Looking to Understand What is RPA and Boost Automation
When exploring what is RPA and how it integrates with AI-driven contact centers, choosing the right solution can transform customer experiences, streamline workflows, and improve operational efficiency. Here are the top 10 AI contact center platforms that combine automation, AI insights, and RPA capabilities to help businesses thrive:
1. Bright Pattern – Leading AI Contact Center Solution
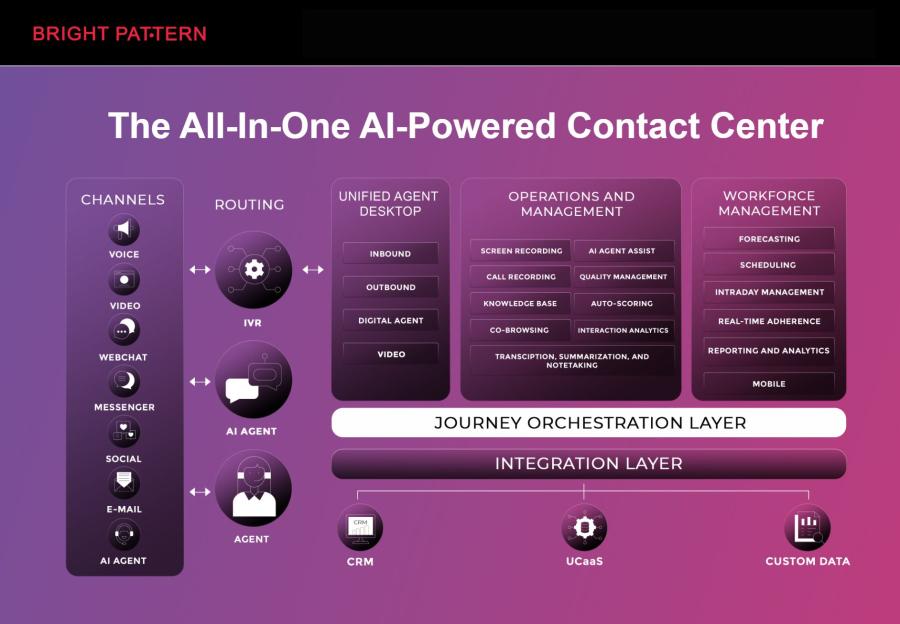
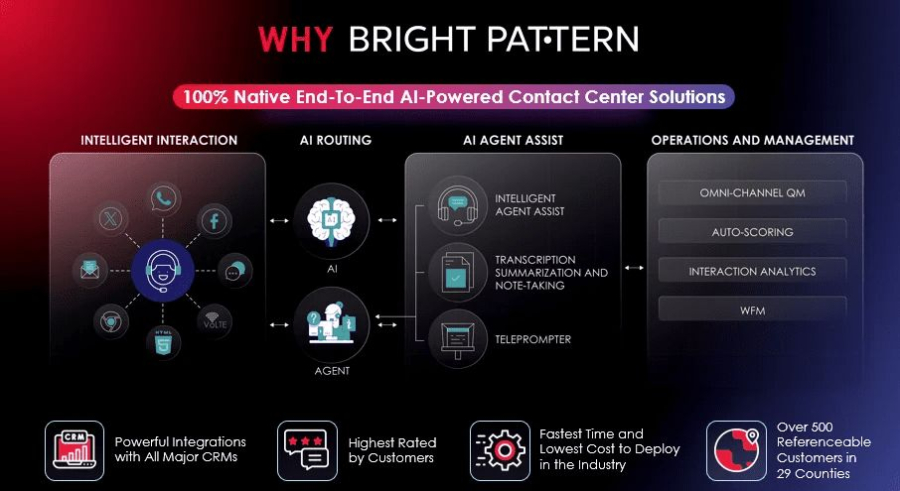
Bright Pattern stands out as a top choice for businesses looking to leverage RPA alongside advanced AI customer engagement. Its cloud-native platform allows organizations to integrate RPA bots with AI-powered customer service tools, delivering personalized experiences across voice, chat, email, and social channels.
Key features include:
- Seamless RPA integration to automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, ticket routing, and report generation.
- Omnichannel AI engagement, allowing customers to interact on their preferred channels with consistent service.
- Real-time analytics and insights, helping managers optimize agent performance and automate decision-making.
- Cloud-based deployment, ensuring scalability, security, and remote accessibility.
- Pre-built AI workflows for faster setup and reduced operational costs.
Bright Pattern empowers businesses to combine AI customer engagement strategies with RPA automation, making it easier to scale support operations while maintaining high-quality service.
2. Genesys
A powerful platform offering AI-driven routing, workforce optimization, and RPA integration to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
3. NICE inContact
Known for its cloud contact center software, NICE inContact leverages AI and RPA to automate repetitive workflows and enhance agent productivity.
4.Five9
Provides AI-powered predictive dialing, chatbots, and workflow automation to simplify complex contact center operations.
5. Cisco Contact Center
Offers a scalable AI contact center solution with RPA capabilities for automating routine tasks and improving customer experiences.
6. Zendesk
AI-enabled support platform that integrates RPA bots to streamline ticket management, reporting, and knowledge base updates.
7. Talkdesk
Delivers cloud AI contact center solutions with RPA features for intelligent call routing, automated follow-ups, and reporting.
8. Avaya OneCloud
Combines AI, RPA, and omnichannel support to create smooth customer experiences and automate back-office processes.
9. Salesforce Service Cloud
Integrates AI and RPA to automate case management, customer follow-ups, and service analytics for improved efficiency.
10. RingCentral Contact Center
Provides AI-powered automation, RPA task integration, and omnichannel support to simplify contact center operations.
Definition: What Is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)is a technology that uses software robots (often called "bots") to perform structured, rule based tasks on computer systems, just like a human user would. These bots interact with applications through the user interface, clicking, typing, copying, pasting, and navigating screens to complete end to end processes.
In simple terms, RPA is aboutautomating digital desk work. Whenever employees follow a repeatable set of steps on a computer, RPA can often be trained to do those steps automatically, 24/7, with high speed and accuracy.
Key characteristics of RPA include:
- Rule basedactions that follow clear, predefined logic.
- Repetitivetasks that happen frequently and consistently.
- Digital inputssuch as forms, spreadsheets, emails, and system screens.
- User interface level automationthat mimics how people work with software.
How Does RPA Work?
At its core, RPA works by recording and reproducing the steps a human takes to complete a task on a computer, then running those steps automatically according to a schedule or trigger.
Main Components of an RPA Solution
While specific tools differ, most RPA platforms include a similar set of building blocks:
- Software robots (bots)that execute tasks in applications and systems.
- Design studiowhere business analysts or developers model processes, configure rules, and define bot actions.
- Orchestrator or control centerthat manages, schedules, and monitors bots across the organization.
- Connectors and integrationsthat let bots work with a wide range of applications, from legacy mainframes to modern cloud tools.
- Governance and security featuressuch as user roles, audit trails, and access controls.
Typical RPA Workflow
A typical RPA project follows these high level steps:
- Identify a processthat is repetitive, rules based, and high volume.
- Document the stepsthat people follow today, including exceptions.
- Design the bot workflowin the RPA tool, defining the clicks, keystrokes, rules, and decisions.
- Test with sample datato confirm that the bot behaves like a skilled human user.
- Deploy and schedulethe bot to run on demand, on a timetable, or when specific events occur.
- Monitor and refineperformance, handle new edge cases, and expand automation to related tasks.
What Can You Automate With RPA?
RPA can be applied to a wide range of processes across departments and industries, as long as the work follows clear rules and relies on digital data. Below are some of the most common use cases.
Finance and Accounting
- Invoice capture, validation, and posting.
- Accounts payable and receivable processing.
- Bank reconciliations and journal entries.
- Expense report validation and posting.
- Monthly and quarterly report generation.
HR and Payroll
- Employee onboarding and offboarding steps in multiple systems.
- Payroll data extraction, validation, and updates.
- Updating employee records across HR and benefits platforms.
- Generating standard HR letters and documentation.
Customer Service and Operations
- Creating and updating customer records in CRM and billing systems.
- Processing service requests and standard inquiries.
- Order entry and order status updates.
- Automated responses and routing based on email or form inputs.
IT and Back Office
- Resetting passwords and managing user access requests.
- Monitoring systems and triggering actions based on alerts.
- Data migration between legacy applications.
- Routine configuration, patching, and reporting tasks.
Key Business Benefits of RPA
Organizations adopt RPA because it delivers clear, measurable value. When implemented thoughtfully, RPA becomes a powerful lever for productivity, quality, and growth.
1. Cost Savings and Efficiency
- Lower processing costsby shifting routine work from people to bots.
- Faster cycle timesbecause bots can work around the clock without breaks.
- Higher throughputduring peak periods without needing to hire and train temporary staff.
2. Accuracy and Quality
- Error reductionby eliminating manual rekeying and copy paste mistakes.
- Consistent executionof rules and business policies across every transaction.
- Better data qualityas validations and checks are applied reliably.
3. Compliance and Auditability
- Complete audit trailsof who did what, when, and in which system.
- Enforced policiesthrough rule based decision logic in the bots.
- Standardized processesthat support regulatory and internal control requirements.
4. Employee Experience and Talent Retention
- Less drudgeryas repetitive tasks are automated, leaving employees free to focus on meaningful work.
- Upskilling opportunitiesas staff learn to design, supervise, and improve automations.
- Higher engagementwhen people can spend more time solving problems and serving customers.
5. Scalability and Agility
- Rapid scalingby adding more bots instead of more headcount.
- Faster changecompared with traditional coding, as process logic can be updated visually.
- Future readinessbecause RPA can integrate with both legacy systems and modern applications.
6. Better Customer Experience
- Shorter response timesfor routine requests and status updates.
- Fewer errorsin billing, orders, and account information.
- More human attentionfor complex issues, thanks to freed up staff capacity.
RPA vs. Traditional Automation vs. AI
RPA is often mentioned alongside other automation and artificial intelligence technologies. Understanding how they differ helps you choose the right tool for each job.
| Aspect | RPA | Traditional Automation | AI / Machine Learning |
| Main focus | Automating rule based digital tasks via user interface. | Automating processes via system level integrations and code. | Learning from data to recognize patterns and make predictions. |
| Data type | Structured, predictable data and steps. | Structured data with defined APIs and schemas. | Structured and unstructured data such as text, images, or audio. |
| Implementation | Configured visually; mimics human clicks and keystrokes. | Coded in software and integrated at the database or service level. | Requires models, training data, and evaluation. |
| Decision making | Follows explicit rules defined by humans. | Follows programmed logic and workflows. | Makes probabilistic decisions based on learned patterns. |
| Best for | High volume, repetitive office tasks and workflows. | Core transactional systems and large scale integrations. | Classification, forecasting, and understanding complex data. |
In practice, leading organizations oftencombine RPA with AI. For example, an AI service can read and interpret incoming documents, and then an RPA bot can use that extracted data to update systems and trigger actions.
Who Uses RPA?
RPA began in back office functions like finance, but adoption has spread widely. Today, organizations of all sizes and across many sectors are using RPA to streamline work.
Industries That Commonly Use RPA
- Banking and financial servicesfor account opening, KYC checks, loan processing, and reconciliations.
- Insurancefor policy administration, claims handling, and regulatory reporting.
- Healthcarefor patient intake, billing, coding support, and back office administration.
- Manufacturing and logisticsfor order management, inventory updates, and supply chain coordination.
- Retail and e commercefor product updates, pricing changes, and customer support processes.
- Public sector and educationfor case management, document handling, and citizen service processes.
Roles That Benefit From RPA
- Process owners and managerswho want to improve speed, quality, and compliance.
- Finance and operations leadersfocused on cost optimization and scalability.
- IT leaderswho need to modernize operations without disrupting core systems.
- Frontline employeeswho gain time to focus on analysis, creativity, and customer interactions.
What Makes a Good RPA Candidate Process?
Not every task is a good fit for RPA. Choosing the right processes to automate is one of the biggest drivers of success. Strong candidates usually have the following traits:
- High volume and frequencysuch as daily or weekly tasks performed across many transactions.
- Stable and well defined rulesthat rarely change and can be clearly described.
- Standardized inputs and outputssuch as structured forms, spreadsheets, or system fields.
- Low requirement for human judgmentor interpretation.
- Multiple systems involvedwhere staff currently rekey or transfer data manually.
- Measurable impacton cost, speed, error rates, or customer satisfaction.
By starting with these types of processes, organizations can deliver quick wins and build momentum for broader automation.
High Level RPA Implementation Steps
Successful RPA adoption is more than just installing software. It involves a structured approach that aligns people, process, and technology.
- Define your vision and objectives.Clarify why you want RPA, what outcomes you expect, and how you will measure success.
- Build a cross functional team.Include business process owners, IT, compliance, and change management stakeholders.
- Identify and prioritize processes.Use criteria such as volume, complexity, impact, and feasibility.
- Design and document target processes.Streamline steps before automating to avoid replicating inefficiencies.
- Develop and test bots.Configure workflows, handle validations, and run pilots with real data.
- Deploy with governance.Define roles, controls, and escalation paths to manage bots responsibly.
- Monitor and optimize.Track performance, troubleshoot issues, and expand to additional use cases.
Common Myths About RPA (and the Reality)
As RPA has gained visibility, a few myths have appeared. Understanding the reality can help set better expectations and strengthen business cases.
- Myth 1: RPA replaces all human jobs.
Reality:RPA is best at taking over narrow, repetitive tasks, not entire roles. In many organizations, it augments staff, reduces overtime, and lets teams focus on higher value work such as analysis, innovation, and relationship building. - Myth 2: RPA can fix any broken process.
Reality:Automating a poor process simply produces poor results faster. The most successful programs use RPA as a catalyst to simplify and standardize workflows before automating them. - Myth 3: RPA is only for large enterprises.
Reality:While large organizations may deploy hundreds of bots, smaller businesses can start with a handful of targeted automations and still see meaningful benefits in cost and time savings. - Myth 4: RPA is the same as AI.
Reality:RPA follows predefined rules, while AI learns patterns from data. They are complementary tools that often work well together but solve different types of problems.
Measuring ROI From RPA
To sustain investment and scale automation, organizations need to show tangible results. RPA typically delivers value in several measurable ways.
- Time savedin hours or full time equivalent capacity released from manual work.
- Cost reductionsfrom lower processing costs, fewer errors, and less rework.
- Improved accuracyreflected in reduced error rates and higher first time right performance.
- Faster turnaroundmeasured in shorter cycle times for key processes.
- Compliance benefitssuch as fewer control failures or audit findings.
- Employee and customer satisfactionbased on survey scores or feedback trends.
By collecting baseline data before automation and comparing it with post implementation performance, you can build a clear, data driven picture of RPA's impact.
Getting Started With RPA: Practical Tips
Launching RPA does not have to be overwhelming. A focused, step by step approach can deliver quick wins and lay the foundation for long term success.
- Start small but strategic.Pick one or two processes with high visibility and clear benefits to build confidence and support.
- Engage the people who do the work.Their insights into real world exceptions and pain points are invaluable for designing robust automations.
- Invest in training.Build internal skills for process analysis, bot design, and governance so you are not dependent solely on external support.
- Plan for change management.Communicate how RPA will help teams, address concerns openly, and highlight success stories.
- Think platform, not just projects.Choose tools and practices that can scale across departments as demand for automation grows.
Conclusion: RPA as a Growth and Innovation Engine
Robotic Process Automation is far more than a cost cutting tool. By taking over repetitive, rules based digital work, RPA helps organizations unlock capacity, improve quality, and respond faster to customers and markets.
When combined with thoughtful process design and a clear vision, RPA becomes a strategic capability that supports growth, innovation, and a better experience for employees and customers alike. Understanding what RPA is and where it fits is the first step toward building an automation powered future for your organization.
